Key Skills: How to discover all of your employees' skills
It’s a big question, one with over 27 million search results on Google alone. With countless definitions, approaches, and methodologies, there are nearly as many answers as there are perspectives on skills and competencies.
Defining skills: Soft, Hard, and "Mad" skills
Understanding the types of skills within an organization helps HR build an inclusive and dynamic skill map. Here’s a breakdown of key skill types:
- Hard Skills: These are technical skills and industry-specific knowledge often acquired through training, education, or hands-on experience. Examples include software development, data analysis, and proficiency in specific tools or platforms. Hard skills are typically measurable and straightforward to assess.
- Soft Skills: Soft skills, or interpersonal skills, refer to qualities that enable effective interaction and collaboration. Examples include communication, problem-solving, adaptability, and leadership. While often harder to measure, soft skills are crucial to creating an agile, collaborative work environment.
- Mad Skills: Mad skills are unique, unconventional skills that bring an innovative edge to an organization. They often stem from unconventional experiences or talents outside the usual scope of work. For instance, a professional with graphic design skills might also have expertise in storytelling or improvisational theater, which could bring fresh perspectives to team projects. Mad skills can enhance creativity and innovation, making an organization more adaptive to change.
Understanding and mapping these three types of skills—hard, soft, and mad—enables HR to fully leverage individual and collective talent in building a skills strategy. Integrating all three into a skills-first strategy offers a competitive advantage and a comprehensive approach to workforce development.
Understanding key competencies and their HR implications
Let’s consider Larousse for a useful definition:
In-depth, recognized knowledge that confers the right to judge or decide in specific matters.
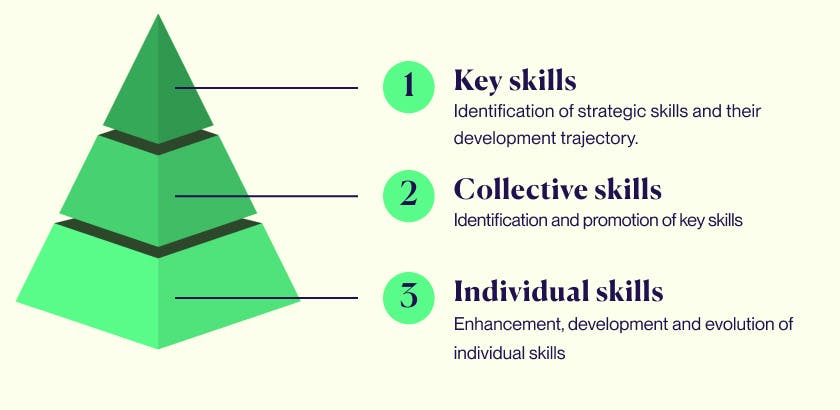
For HR professionals, competencies break down into three main categories: individual, collective, and key.
- Individual competence: This includes knowledge developed through training and experience, applied to fulfill tasks or projects.
- Collective skills: Collective skills refer to a team’s combined competencies, where cohesion amplifies effectiveness.
- Core competencies: Core competencies represent the skills that give a company its competitive advantage and ensure sustained performance. To foster them, organizations must have a robust strategy in place.
The commonality between these definitions lies in their cohesive structure: while individual skills provide a foundation, core competencies emerge from a strategic, company-wide approach.
Building a skills pyramid
The concepts of growth and learning play a pivotal role in developing individual competencies. Training and experience, two levers HR can pull, are essential to fully leverage employees’ capabilities. Additionally, collective skills help HR identify key competencies critical for organizational success.
Skills development: Empowering employees for growth
An effective skills development strategy is essential for building resilience, retaining talent, and maintaining a competitive advantage. HR can drive skills development through a variety of methods:
- Training and Upskilling: Continuous learning is vital. Offering both formal training and on-the-job learning opportunities allows employees to strengthen and expand their hard and soft skills. Upskilling programs, whether through internal training modules, external courses, or certifications, are particularly effective for developing industry-specific competencies.
- Personalized Learning Paths: By leveraging data-driven insights from Skills Intelligence platforms, HR can tailor development opportunities to each employee’s needs and career aspirations. Personalized paths enhance engagement and encourage employees to take ownership of their growth.
- Mentoring and Cross-Functional Collaboration: Mentoring programs and collaborative projects facilitate the exchange of soft skills and mad skills. This approach not only develops competencies but also fosters a culture of knowledge-sharing and innovation.
- Internal Mobility: Internal mobility is a powerful tool for skills development, allowing employees to explore new roles, gain diverse experiences, and apply their skills in different contexts. Mapping skills and aligning them with internal opportunities supports career progression and reduces turnover.
By investing in a structured skills development program, HR can ensure that the organization’s talent remains agile and prepared to adapt to industry changes.
Competence: the most sought-after competitive advantage
The strategic value of competencies cannot be overstated, as demonstrated by successful acquisitions focused on skill acquisition:
- The Walt Disney Company: Through acquisitions like Marvel and Pixar, Disney diversified its capabilities, gaining industry expertise and creative talent.
- Amazon: Since its founding, Amazon has acquired over 80 companies, especially in logistics and robotics. The 2012 acquisition of Kiva Systems, for instance, has allowed Amazon to automate and streamline its operations.
In both cases, these companies invested in key skill acquisition to meet strategic objectives. For organizations today, competencies are invaluable assets that HR leaders must recognize and nurture.
Identifying key skills in your organization
Skill identification and self-declaration are vital for empowering employees to take an active role in their development. By involving them continuously in your skills identification process, you gain a living map of current capabilities and can anticipate future needs.
At 365Talents, we empower employees to express their skills transparently and inclusively, regardless of language, location, or experience level.
However, challenges exist in skill identification, especially with self-declaration. Employees may describe the same skill differently: “project management” might also be termed “project coordination” or “project leadership.” This variation complicates tracking and categorizing skills effectively. The true goal lies in mapping potential based on experience to build effective teams and drive strategic initiatives.

Choosing the right solution
At 365Talents, we believe in the freedom for employees to define their skills authentically: Project Manager, Organizer, Excel Expert, or To-Do List Champion. Our AI-driven platform captures these unique expressions, aligns them with organizational needs, and connects them to real opportunities.
Depending on your time frame and organizational needs, there are three main approaches to skills management:
- Short-term: Skills Repository by Sector
- Advantages: Pre-built with key sector-specific skills.
- Drawbacks: May lack personalization and can be difficult to tailor.
- Medium-term: Consulting Expertise
- Advantages: Offers an external, objective viewpoint.
- Drawbacks: High costs and long timelines, with a risk of data obsolescence.
- Long-term: Custom Dynamic Skills Repository
- Advantages: Real-time, employee-driven, and integrates with existing tools.
- Drawbacks: Initial costs and AI-related concerns.
For organizations seeking future resilience, a custom, dynamic skills repository powered by Skills Intelligence is an invaluable long-term asset.
Dynamic skills repository by 365Talents
Our solution enables you to create a dynamic, open skills repository in any language and integrates seamlessly with your HR data. By engaging employees in the process, our platform provides a constantly evolving, customized view of skills across your organization.
With a comprehensive view of your workforce's skills, you can align these with strategic needs, making skills management a cornerstone of your talent strategy.
Your best ally: Skills Intelligence
Skills Intelligence helps you leverage employee data from annual reviews, training, projects, and feedback across all platforms (LMS, HCM, project management tools). It allows you to offer employees opportunities that align with their current skills and future career aspirations. With Skills Intelligence, data analysis becomes straightforward and can be directly applied to strategic HR issues like Workforce Planning.
Since its launch four years ago, the 365Talents platform has enabled Société Générale’s HR team to transform its skills mapping, achieving:
- 45,673 employees onboarded
- 5,114 internal mobility opportunities
- 2/3 of suggested skills rated as relevant by employees
- 3,771 average interactions with opportunities
- 100% of positions consistently mapped
Real-time skills mapping for real-time strategy
To maximize the value of skills data, consider these critical questions:
- Are your skills data current?
- What systems are in place for data updates, and at what cost?
- Does your system account for all competencies, including soft skills?
- How effectively does it identify skills gaps and anticipate future needs?
Our world—and your teams—are in a state of continuous evolution. That’s why forward-thinking companies choose 365Talents for intelligent skills and career mapping. With us, your organization can stay agile and ready for tomorrow.
Discover more HR insights