The guide to Skills Mapping for HR professionals
Welcome to the evolving world of skills mapping! As we dive into this critical aspect of talent management, it's essential to understand how skills mapping can transform your HR practices and contribute to a more agile and dynamic workforce. Whether you're just starting out or looking to refine an existing framework, this guide will cover the fundamentals, explore various approaches, and address common pitfalls to ensure you build a robust skills map for your organization.
Understanding Skills Mapping
What is skills mapping?
Skills mapping is a comprehensive process that involves defining, organizing, and managing the skills within an organization. It serves as a foundation for addressing various HR challenges by linking skills with job roles, career development, and organizational strategy.
Key terms to know:
- Skills Library: A static collection of categorized skills used for reference.
- Skills Referential: Similar to a library but often more dynamic in how it integrates skills.
- Skills Ontology: A more complex model that explores the relationships and dependencies between skills.
- Skills Framework: A structured approach that defines, relates, and applies skills within organizational contexts.
In practice, many organizations use the term "skills map" to describe a dynamic and interactive model that connects skills with job roles and career paths, offering a more holistic view compared to static libraries or frameworks.
Why skills matter
Understanding and effectively managing skills is increasingly crucial in today’s work environment. Research shows that a staggering 80% of executives believe their workforce is not fully utilizing its skills, highlighting a significant opportunity for improvement. With core skills evolving every every five years, staying up to date is critical. Adopting a skills-based approach not only helps organizations retain top performers but also enables them to adapt to industry changes more effectively.
Approaches to building a skills map

1. Top-down approach
This method begins with strategic alignment from the leadership team. It involves:
- Setting strategic goals.
- Identifying critical skills that align with business objectives.
- Consolidating existing skills and job frameworks.
- Matching these skills to key roles.
- Conducting employee self-assessments and managerial reviews to identify skills gaps.
Benefits:
- Ensures alignment with strategic goals.
- Identifies the critical skills required for business success.
Drawbacks:
- It may not fully capture the day-to-day operational needs.
- It could overlook emerging skills not yet recognized by leadership.
2. Bottom-up approach
This approach focuses on gathering detailed, grassroots-level information by:
- Conducting employee self-assessments and managerial reviews.
- Using questionnaires and specialized HR softwares to collect data.
- Building a skills inventory and creating a comprehensive skills framework.
- Relating skills to roles and integrating insights with strategic objectives.
Benefits:
- Reveals hidden talents and provides a detailed view of existing skills.
- Offers a bottom-up perspective that can complement top-down insights.
Drawbacks:
- It’s time-consuming to gather, validate, and analyze the data.
- It may require significant efforts to consolidate and integrate the information.
3. Technology-driven approach
This approach leverages advancements in machine learning and AI. It:
- Uses existing data sources like job descriptions, employee declarations, and open positions to infer skills.
- Automates the mapping of skills to jobs and roles.
- Utilizes technology to conduct employee assessments and manage skills data.
Benefits:
- Automates and enhances the skills mapping process.
- Particularly useful for large organizations with complex skill needs.
Drawbacks:
- The initial setup and integration of technology can be complex.
- It requires an investment in specialized software and tools.
Common pitfalls in Skills Mapping
- Poor job architecture documentation: Incomplete or missing job descriptions make it difficult to identify required skills.
- Multiple skills frameworks: Managing various skills taxonomies can lead to inconsistencies and confusion.
- Time-consuming processes: Manual skills mapping can be labor-intensive and often leads to lengthy discussions and delays.
- Language barriers: For multinational organizations, accommodating multiple languages within skills frameworks can be challenging.
- Outdated frameworks: Ensuring that the skills framework remains current and reflects organizational changes is crucial.
These challenges can be exhausting for HR teams. For large companies, it is a nightmare. To avoid them, HR technology vendors offer solutions that simplify skills and job mapping, providing dynamic frameworks that are always up-to-date!
How to choose your skills mapping tool?
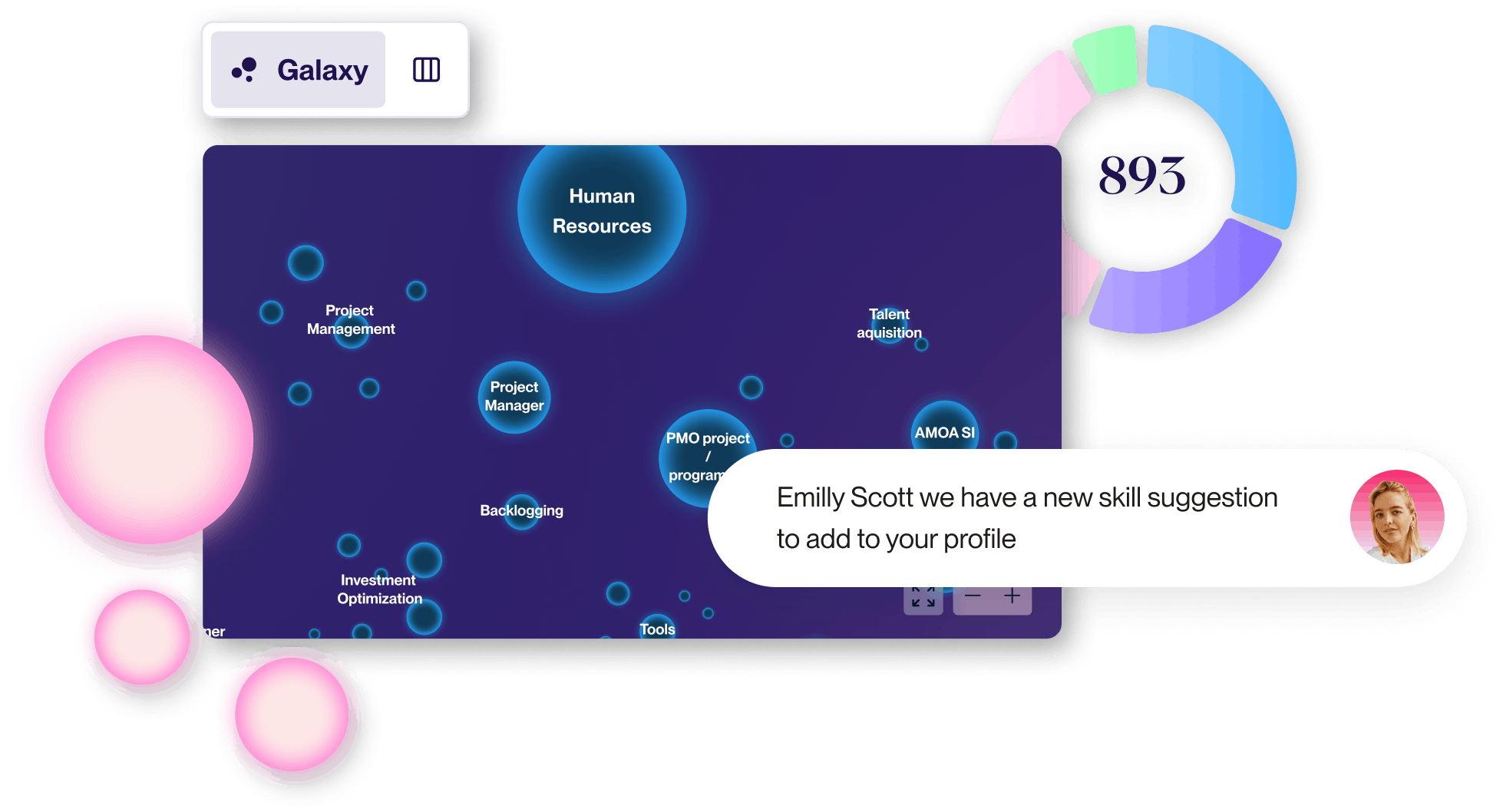
But first, what is a skills mapping tool?
Skills mapping tools simplify the process of identifying, organizing and aligning the skills, knowledge, and competencies required for each role and team within an organization. These tools enable a clear comparison between current skill sets and the skills needed, allowing for more strategic recruitment and personalized training programs to close any gaps. With features designed to cater to specific roles, team dynamics, and individual career growth, skills mapping tools play a crucial role in enhancing workforce capabilities and driving talent management efforts.
Solutions and best practices to map your skills
At 365Talents, we address these common challenges by:
- Ensuring skills frameworks are accurate and exhaustive.
- Automating skills data management, including translations and deduplication.
- Benchmarking skills against industry standards.
- Using generative AI to create job descriptions and offer multilingual support.
- Integrating with other HR systems for a seamless, cohesive approach.
Success Stories
To demonstrate the real-world impact of these concepts, here are two success stories from our clients.
- Global Banking Group: One of the world's largest banking groups implemented a common skills ontology across its 39 regional banks. By leveraging 365Talents' technology, they established a unified skills language, enabling regional banks to maintain local specificity while synchronizing with the global taxonomy. This approach facilitated better strategic decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Global Energy Leader: A major player in the energy and utilities sector aimed to enable employees to declare their skills in their native languages (Spanish, French, and English). 365Talents developed a solution that automated the translation and data management processes, significantly reducing manual work while increasing the accuracy of the skills data.
Engaging your business Team
To effectively pitch skills mapping to your board or executive team, it's crucial to highlight its strategic importance. Skills mapping can support various business needs, including:
- Company Pivoting: Adapting to market changes or strategic shifts.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Integrating new teams and aligning skills.
- Innovation: Supporting the adoption of new technology and process.
- Sustainability and Transformation: Aligning skills with organizational goals in sustainability and green initiatives.
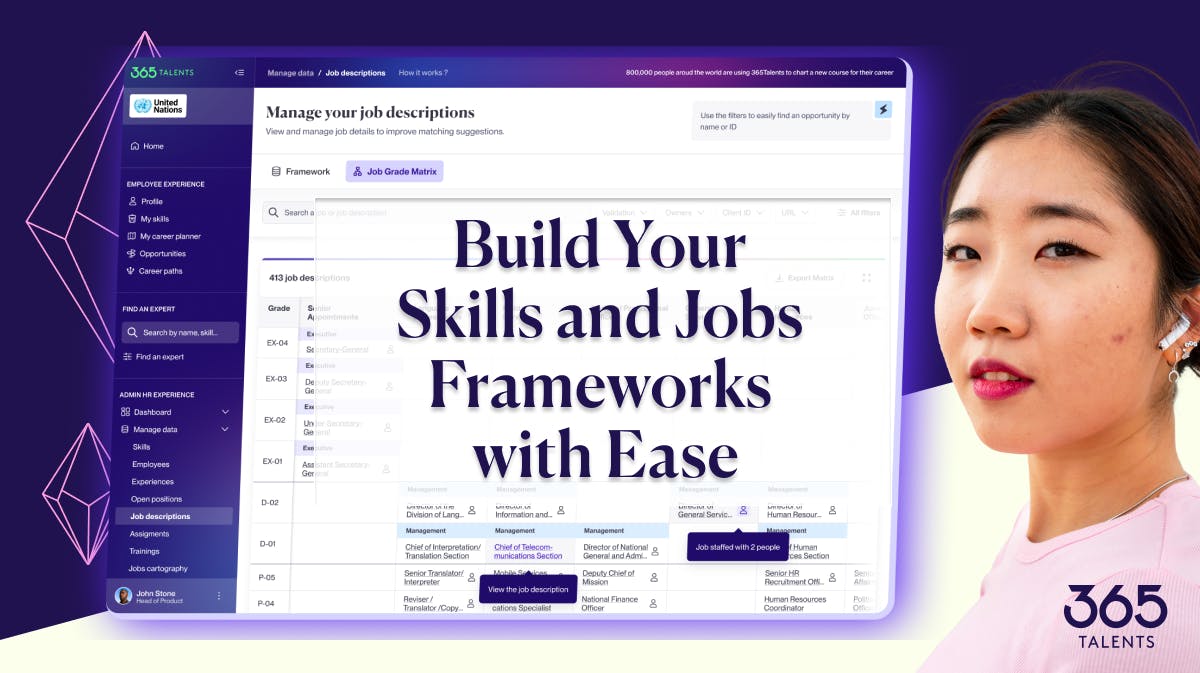
Your Skills and Job Architecture with 365Talents
365Talents offers an AI-powered solution designed specifically for HR teams to easily create tailored skills and job architecture that align your organization’s unique needs.
By blending advanced AI-driven technology with profound human expertise, we provide a customized framework that serves as a solid foundation for your skills and job architecture. Our solution supports your organization’s growth, seamlessly integrating with your systems while enhancing learning, performance, and workforce mobility.
No data? No problem.
Regardless of where you are in your data journey, 365Talents delivers the technology and expertise to help you build a unique skills and job architecture tailored to your organization.
We start by centralizing your job data, even if it's fragmented or incomplete. Our AI-powered platform organizes and structures this data, creating the first version of your job architecture while defining key skills and proficiency levels.
At the same time, we develop a comprehensive skills ontology that aligns with your roles. This includes dynamic visualizations of your skills and job data (Skills and Job Galaxies), highlighting relationships and skills gaps, and uncovering development opportunities across your workforce.
Book your demo to learn more about Skills and Job Architecture solution!
Conclusion
Skills mapping is not just a theoretical exercise but a practical tool that can significantly enhance how organizations manage talent. By understanding and implementing the right approach—whether top-down, bottom-up, technology-driven, or a mix of all three—HR professionals can better align skills with business objectives, address gaps, and drive organizational success. As you embark on or refine your skills mapping journey, remember that it’s a collective project involving business leaders, HR professionals, subject matter experts, and employees. Embrace the process, and let it guide your organization towards a more agile and effective future.

FAQ
How do you distinguish between competencies and skills?
While often used interchangeably, skills and competencies have distinct meanings within the realm of talent management and workforce development.
- Skills refer to specific, measurable proficiencies acquired through practice, education or experience. They are task-oriented and can range from technical abilities to soft skills such as leadership or problem-solving.. For example, being able to effectively lead a team is a skill.
- Competencies, on the other hand, are more holistic and multifaceted. They combine skills, knowledge, attitudes and behaviors needed to perform a task or role effectively. For instance, in healthcare, patient care competencies would include a set of skills and knowledge needed to provide a comprehensive service.
What’s the best approach for updating job titles, job descriptions, and skills referentials?
Here’s a recommended approach:
- Job titles and descriptions: Begin by updating job titles and descriptions. If you have existing skills frameworks, you can integrate it during the update. If not, focus first on creating a solidjob architecture, then define the skills associated with each role.
- Skills referential: Once the job architecture is in place, develop and refine the skills referential. Ensure it aligns with the newly updated job titles and descriptions.
This approach ensures a structured process for building both your job architecture and skills framework cohesively.
How many skills should be identified per job role?
Generally, it’s effective to associate around 10 to 15 key skills with each job role. Having fewer skills might lead to incomplete data, while more than 15 can be overwhelming for employees to declare and for the system to manage. A typical recommendation is about 12 skills per job role for a balanced approach.
How do you ensure that job descriptions are relevant and accurately reflect current roles?
Ensuring job descriptions are relevant involves a few key steps:
- Governance and review: It's crucial to have strong governance around both your skills framework and job architecture. If you notice that some job descriptions are poorly written or outdated, it’s important to address this by reviewing and revising them. One of our customers, a European leader in the railway industry, emphasized the need for clear governance around job architecture to maintain accuracy and relevance.
- Leveraging technology: Utilize technology to assist in generating and refining job descriptions. For instance, AI tools can create or improve job descriptions based on job titles and core responsibilities. This approach can provide a baseline that can be further refined by human review.
At 365Talents, we use our platform to draft and then enrich job descriptions. As a manager, you’ll receive an initial draft based on existing data, which will then be enhanced by using generative AI. This approach will allow you to quickly review and adjust the descriptions, making the process more efficient and accurate.
How do you calibrate proficiency ratings across the organization to ensure consistency?
Calibrating proficiency ratings involves standardizing and clearly defining levels across the organization:
- Standardized proficiency levels: Typically, proficiency levels are categorized into four stages (e.g., Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced, Expert). This four-level system helps avoid the ambiguity that can occur with fewer levels.
- Detailed descriptions: Each proficiency level should come with a detailed description outlining what is expected at each stage. For example, a beginner might need to have completed specific e-learning courses, while an intermediate level might require practical assignments or projects. These descriptions help ensure that employees and managers have a clear understanding of what each proficiency level entails.
- Consistency in tools: Our platform includes standardized titles and descriptions for proficiency levels. This ensures that when employees self-assess or managers evaluate skills, there is a common understanding of what each level means. Additionally, providing detailed descriptions for skills helps clarify what is required for each one.
By implementing these practices, organizations can maintain a consistent and accurate approach to proficiency ratings, which supports fair and effective skills assessments.
Discover more HR insights