Your skills-based guide to the 9-box grid for talent management

The 9-box grid is a popular talent management tool that provides organizations with a simple framework for measuring employee performance and potential.
HR teams typically use the 9-box grid to inform their approach to:
- Succession planning
- Talent management
- Learning and development
In this article, we’ll outline the benefits and limitations of the 9-box grid, and provide some top tips on how to use it effectively.
What is the 9-box grid?
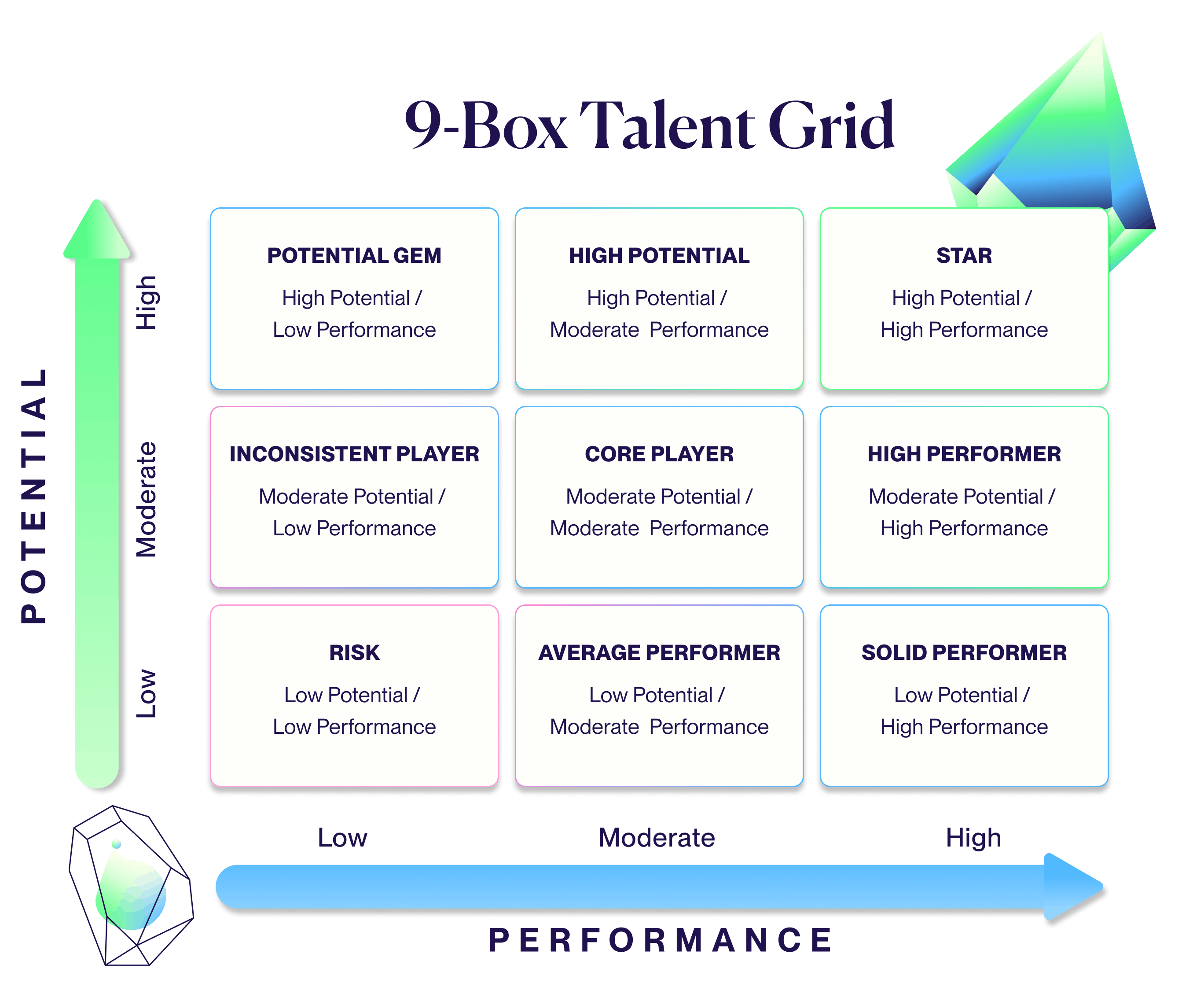
As shown below, the 9-box grid positions employees across nine key data points. The x-axis (horizontally) plots employee performance and the y-axis (vertically) plots employee potential. The resulting nine boxes in the grid enable organizations to pinpoint the relationship between the two.
- A high-performing employee with high potential will appear in the top right-hand box of the grid. These employees excel in all aspects of their roles and are most likely to progress into leadership positions.
- A moderate performer with moderate potential will appear in the middle box of the grid. With the right guidance, training, and support, these employees could deliver more.
- A low-performing employee with low potential will appear in the bottom left-hand box of the grid. These employees are often “bad hires”. They may need to be reassigned to more junior positions or, in the most extreme cases, be removed from the business entirely.
And so on…
What are the benefits of the 9-box grid?
The 9-box grid promises several benefits to HR teams:
1. Easy to use
The 9-box grid presents organizations with core employee data in an easy-to-view and easy-to-understand format.
The system is well established, which means HR professionals need only assess and score their employees as they see fit and plot them into the correct box.
Anyone new to the concept, or new to a particular organization, can quickly catch on and gain valuable insights about the workforce. For this reason, HR teams often leverage the 9-box grid for conversations with senior leaders and members of the C-suite.
2. Enables a holistic approach to workforce management
HR teams benefit from an immediate and comprehensive view of the entire workforce, and they can also create alternate grids for different departments, teams, levels of seniority, and regions. This makes it easy to pinpoint areas of weakness within the workforce and where there are opportunities for employee development.
Reviewing employees in this format also encourages a more balanced approach to performance management. For example, an employee’s potential to be a star performer can be brought to light, even if they seem to be struggling when it comes to their day-to-day duties.
3. Drives fruitful conversations among leadership teams
Establishing a 9-box grid compels HR and leadership teams to communicate openly and honestly about the workforce and reach a consensus on performance expectations.
Not only does this ensure that employees are rated using consistent criteria, but these conversations may help teams to redefine long-term goals and shape the overall business strategy.
4. Workforce planning made easy
A better understanding of the workforce informs better long-term business decisions.
HR teams can make data-driven decisions about learning and development opportunities, promotions and mobilities, and the company’s leadership pipeline. Employees who require additional support to deliver their best work are quickly identified, while those who are already thriving can advance more quickly through the ranks when internal positions come up. Given that recruiting and onboarding external talent are often huge drains on business resources, it is especially useful for HR teams to have this information to hand.
In addition, when organizations know how to direct their resources intelligently, they enjoy a better return on investment. A junior employee who is already working at their maximum potential, for example, should not be put forward for leadership development opportunities.
What are the limitations of the 9-box grid?
The 9-box grid is not without its drawbacks.
1. Vague metrics
The 9-box grid has been criticized for its use of vague and non-objective metrics. Is it possible for organizations to definitively measure an employee’s potential? And how is performance distinguished from potential?
2. Unconscious bias
If organizations do fail to develop objective criteria to assess the workforce, the 9-box grid may invite unconscious bias.
Prejudice, personal opinion, and favoritism should have no bearing on where someone lands on the grid, but it’s all too easy for these biases to slip in. A manager that shares interests, life experiences, and educational background with a particular employee is unlikely to rank them as anything other than high-potential.
3. Pigeon-holing employees
Labels are hard to shake, particularly the bad ones.
When an employee deemed low-potential is placed on the grid, it could irreversibly affect how they are perceived by their teammates, manager, and other senior leaders. Their contributions might be dismissed and they are much less likely to be considered for important projects or promotions.
On the other hand, a high-potential employee with a bad attitude might be granted allowances or additional support that are not awarded to their less capable peers.
4. Employee motivation
Organizations that opt for total transparency surrounding the 9-box grid, run the risk of alienating or demoralizing certain employees. While low-performing and/or low-potential employees certainly present challenges, labeling them as such could only serve to exacerbate the problem.
In addition, choosing to rank employees so openly may encourage unhealthy competitiveness, disrupting workplace harmony and stifling collaboration.
How to use a 9-box grid to maximize benefits
Step 1. Define goals
As with the implementation of any new HR process, begin with clearly defined goals.
For example, an organization that intends to use the 9-box grid for succession planning can focus on evaluating specific skills and leadership potential.
To inform the implementation of learning and development programs across the entire organization, a more holistic approach and change management will be required.
Some organizations choose to customize each square of the 9-box grid to suit their unique business goals.
For example, employees in the top right-hand box (high performers with high potential) could be labeled “Stars”, “Leadership Pipeline”, or “Up for promotion.” Those in the bottom right-hand corner (low performers with low potential) could be labeled “wrong hires”, “on probation”, or “relocate."
Further, organizations that do intend to share the results of the 9-box grid with the workforce ought to carefully choose the terminology they use to encourage, rather than disparage, employees.
Step 2. Objectively assess performance and potential
To ensure that 9-box grid data is fair, consistent, and reliable, develop prescriptive benchmarks and assessment criteria for assessing employee performance and potential.
The biases of individual managers are much more likely to impact how an employee is scored for potential. One way to combat this is to appoint a panel of diverse assessors who can discuss the following:
- Is the employee’s current role allowing them to progress further?
- Might this employee be better suited to another role?
- Has this employee been given the right guidance and support?
- Does the employee express interest in acquiring new skills and/or long-term career progression?
However, this approach is especially time-consuming and can not promise to fully eliminate unconscious bias.
Investing in digital solutions, such as a skills assessment tool, is perhaps the most effective method for evaluating potential since it can assess employee potential quickly, accurately, and with total impartiality.
An HRIS is an all-in-one tool which fuels HR processes and workflows for recruiting, onboarding, performance, compensation, learning, succession and development. Integrating with a talent experience solution like 365Talents optimizes the talent management process with smart skills intelligence and opportunity suggestions to boost internal mobility and optimize career development planning.
When you integrate 365Talents with your HRIS, you seamlessly connect and enhance your existing HRIS tools, enabling your HR, managers and employees to harness the full potential of skills-based decision-making.
For employees and managers, integration with 365Talents connects your platforms to better offer highly personalized job, career path, project and learning recommendations. The option for visual integration with your HRIS also creates a centralized and unified user experience for your people to improve adoption and activation rates on your HR tools.
For HR, integration creates a streamlined process and leverages 365Talents’ Skills & Jobs intelligence to increase employee engagement on profile completion, optimize performance reviews, foster learning and career development and boost internal mobility.
365Talents integrates with SAP SuccessFactors, Oracle and Altays, among other popular HRIS solutions.







How to complete the 9-box grid example
To evaluate performance…
- Low-performance employees do not fulfill the requirements stated in their job description and fail to meet targets and goals. They do not respond positively to feedback and guidance.
- Moderate-performance employees meet a portion of the requirements stated in their job description and meet select targets and goals.
- High-performance employees meet and exceed the requirements stated in their job description, going above and beyond to excel in all aspects of their roles.
To evaluate potential…
- Low-potential employees may already be working at their maximum potential or have no desire to further advance their careers and/or skill set.
- Moderate-potential employees have a lot to offer a business but they are unlikely to assume the most senior roles in the business.
- High-potential employees are those destined for workplace success. Already performing way beyond their role and pay grade, these are the people organizations want in their leadership pipeline.
Step 3. Put a plan into action
This final step happens once all employees have been assessed and plotted onto the 9-box grid.
Depending on what the grid reveals about the workforce and its employees, organizations might decide to:
- Invest in skills and development training with upskilling and reskilling plans
- Develop a robust leadership pipeline
- Conduct performance reviews to determine obstacles to success
- Relocate employees to better-suited positions or departments through internal mobilities
- Place employees on probation
- Initiate the process to remove employees from the business
In encouraging HR teams to focus on people development, the 9-box grid enables organizations to achieve both their people and business goals.
Want to learn more about optimizing your HR processes through skills-based strategy and tools? Get in touch with 365Talents today.
Uncover more HR insights